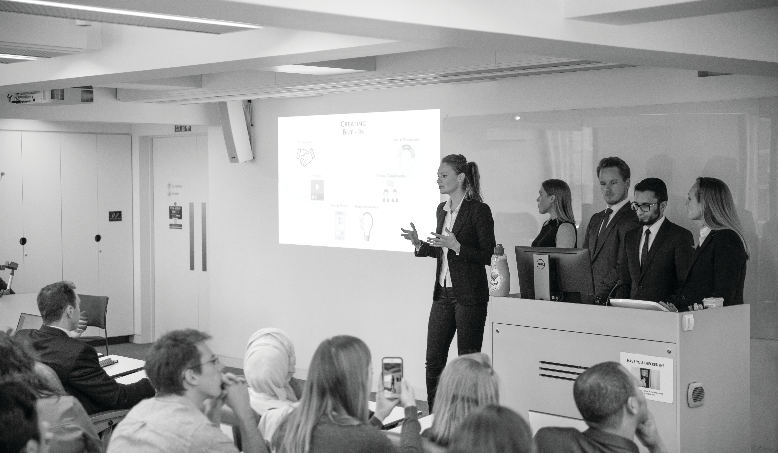
What is business analytics?
Business analytics is the practice of using data and statistical methods to gain insights and make informed decisions in a business setting.
Every business collects data, whether it’s sales data, customer feedback, website traffic, player performance, etc. Business Analytics involves take that data and analyzing it in a way that provides useful information and ideally, something actionable. For example, a company may use analytics to see which products are selling best, which customers act like each other, or which marketing campaigns are most effective.
The analysis typically involves using tools like statistical models, data visualization, and machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and trends in the data. The goal is to turn the raw data into actionable takeaways that can be used to make better decisions and drive the business.
What is interesting to many, is that business analytics is not a vertical – it’s a horizontal subject. This means that you can use business analytics across a wide range of industries, including finance, healthcare, retail, and more. By using data to inform decision-making, companies can optimize their operations, improve their products and services, and ultimately, leading to key measures of increasing revenue or reducing cost.
How does Business Analytics Work?
Let’s simplify with a simple framework we follow.
- Define the business problem
- Confirm availability of data, skillsets needed, time and budget
- Collect and clean the data
- Create a Minimal Viable Product (MVP)
- Gather stakeholder feedback on the MVP
- If approved, then plan for automation or production
- Strategy is changed and new processes must be created with proper documentation
- Optimize per agreed upon time of the stakeholders
What methods exist for data analysis?
How is the initial analysis collected? It varies from business to business, but many companies use predictive modeling. This method can be complex and is used to make decisions in real-time that are informed by patterns accurately reported by informed reports. Other methods are varied in their sophistication—you can predict data with artificial intelligence or even a spreadsheet with a statistical function.
Types of Analytics:
- Descriptive analytics: Focused on summarizing historical data and understanding what happened in the past. Descriptive analytics can help you identify trends, patterns and anomalies in your data and is often used to create reports and dashboards that provide insights into business performance.
- Diagnostic analytics: Focused on understanding why something happened in the past. It involves drilling down into the data to identify the root causes of a particular trend or pattern. Diagnostic analytics can help you uncover the factors that are driving business performance and identify areas of improvement.
- Predictive analytics: Focused on forecasting what is likely to happen in the future. It involves building statistical models that use historical data to make predictions about future events. Predictive analytics can help you identify opportunities and risks, and make the data-driven decisions to optimize business performance.
- Prescriptive analytics: Focused on recommending actions to take based on the insights gained. It involves using optimization and simulation techniques to identify the best course of action to achieve a particular business goal.
This is also known as the maturity curve of analytics.
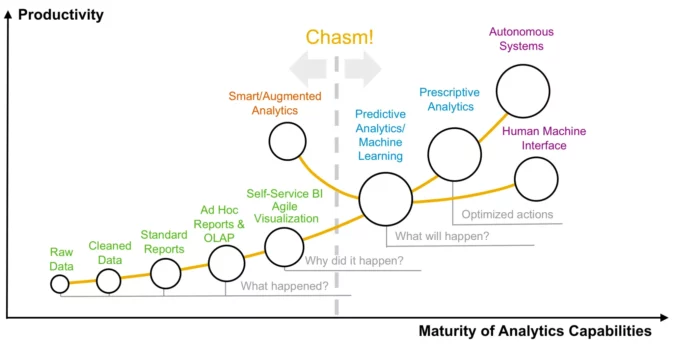

Source: Predictive Is The Next Step In Analytics Maturity? It’s More Complicated Than That!
What jobs can you get with a business analytics degree?

Want to know what jobs you can get with a degree in business analytics? Here are some of the most popular jobs that business analytics students get post-graduation.
Operations Analyst
An operations analyst is a crucial member of a business team who helps identify areas for improvement and cost-saving opportunities. They dig deep into how things are done, analyze data, and find ways to make processes run smoother and more efficiently. They work closely with other teams and keep track of how things are going to make sure changes are making a positive impact. To be successful in this role, it’s important to be a good communicator, have strong problem-solving skills, and be great at analyzing data.
Data Analyst
Data analysts are like detectives for businesses, using their skills to uncover insights hidden in large datasets. They’re experts at using tools like SQL, Excel, and statistical software to find patterns and trends in data, and then sharing their findings with stakeholders. They also use visualizations and dashboards to help non-technical team members understand what they’ve found. They might also run experiments, build models to predict future outcomes, and suggest ways to improve business processes based on their findings. To be a great data analyst, you need to be an excellent problem solver, have top-notch analytical skills, and be able to communicate clearly and effectively.
Supply Chain Analyst
Supply chain analysts are the people who keep things moving smoothly from the supplier to the customer. They look at all kinds of data, like production schedules and transportation systems, to find ways to make the supply chain work better. They work closely with other teams to create new procedures and improve existing ones, and they’re also in charge of forecasting demand and keeping inventory levels just right. Being a great supply chain analyst takes a sharp eye for detail, strong problem-solving skills, and a knack for analyzing data.
Operations Manager
Operations managers are the ones who keep an organization’s day-to-day operations on track. They’re responsible for managing staff, creating policies and procedures, and keeping an eye on how well everything’s going. They’re also great at working with other teams to plan for the future, manage budgets, and make sure everyone has what they need to do their jobs. To be a great operations manager, you need to be an excellent communicator, have strong leadership skills, and be a great problem solver. You can find operations managers in all kinds of industries, from healthcare and hospitality to logistics and manufacturing.
Marketing Analyst
Marketing analysts are experts at understanding customer behavior and finding ways to reach them effectively. They use all kinds of tools, like surveys, focus groups, and web analytics, to uncover insights and develop strategies. They’re also great at working with other teams to create marketing campaigns, track how well things are going, and find ways to make things even better. To be a great marketing analyst, you need to be creative, have top-notch analytical skills, and be a great communicator. You can find marketing analysts in all kinds of industries, from retail and finance to technology and beyond.
Business Analyst
Business analysts are organizational superheroes who collect and analyze data from various sources to solve problems and improve operations. They collect and analyze data from a wide range of sources, such as financial reports and customer feedback, to gain insights and find opportunities for improvement. Working closely with cross-functional teams, business analysts help design and implement business processes, systems, and strategies that drive success. They may also be involved in project management, risk assessment, and change management. Strong analytical, problem-solving, and communication skills are essential to excel in this role.
Management Consultant Analyst
Management consultant analysts offer expert advice to companies to help them achieve their goals. They analyze everything from organizational structures to operations and strategies to identify areas for improvement. They can also help with managing changes in the organization, optimizing processes, and reducing costs. To succeed in this role, you need to be a jack-of-all-trades. You need excellent analytical skills, the ability to communicate effectively, and be a problem-solving pro. If you’re up for the challenge, you could work for consulting firms or be an independent contractor and serve clients across different industries. Being a management consultant analyst is a rewarding and challenging career choice for those looking to make a difference in the business world.
Financial Analyst
These are the experts who analyze financial data to provide guidance to individuals, investors, and companies. They get their hands dirty, gathering and interpreting data from financial statements, economic trends, and market conditions. They use all this data to identify investment opportunities, evaluate risks, and make financial forecasts. Financial analysts can specialize in specific industries or market sectors, such as healthcare or technology. They’re also the people to turn to for advice on financial planning, mergers and acquisitions, and portfolio management. To be successful as a financial analyst, you need to be a master of math, analytics, and communication. You could work for investment firms, banks, corporations, or many other organizations.
CRM Analyst
CRM Analyst are a secret weapon for businesses that can optimize customer experiences and fuel a company’s growth. They’re the ones who dive deep into customer data, spotting trends and insights that drive positive outcomes for businesses. Working with cross-functional teams, they design and implement strategies that improve customer engagement, retention, and loyalty. They’re always on the lookout for new opportunities to enhance the customer experience. CRM analysts use tools like customer feedback surveys, web analytics, and marketing automation software. They need to have a sharp analytical mind, be able to solve complex problems, and have a keen eye for detail. RM analysts are found in various industries like retail and finance, where they’re in high demand.
Data & Analytics Manager
As a Data & Analytics Manager, you’re responsible for managing and overseeing all the data and analytics functions. You develop and implement data strategies, design and maintain data systems, and analyze data to identify insights that you communicate to internal and external stakeholders. This role is like the master architect of data models and governance measures that ensure data security. You’ll need strong leadership, project management, and analytical skills to navigate your ship through any challenges that come your way. It’s their job to ensure that all data-driven decisions align with the overall goals and objectives of the organization. If you’re looking for a role that offers challenge, responsibility, and the chance to make a real impact, being a Data & Analytics Manager is a great option.
Data Scientist
Data Scientists are the Sherlock Holmes of the business world, sifting through complex data sets to uncover hidden trends and insights that can improve business processes and outcomes. You’ll use statistical and machine learning techniques to turn data into actionable insights. Like master craftsmen, they design and implement models and algorithms to solve business problems. But the real artistry lies in their ability to present these insights and recommendations to stakeholders in a way that is easy to understand and drives positive change. Data Scientists work with large and varied datasets, using tools like Python, R, and SQL to transform data into valuable insights. Success in this role requires strong analytical, problem-solving, and communication skills. Wherever they work, their goal is always the same: to use data to improve business outcomes.
What programs are available at Hult for studying business analytics?
To nail a job in business analytics, you will almost certainly need a degree. It is important you are aware of the range of programs available to you. Hult offers a Master’s in Business Analytics, as well as a Bachelor’s in Business Administration where you can major in business analytics, and MBA programs where you can take electives in business analytics. While these courses are unique and exclusive to Hult, it is a widely taught practice at business schools and has courses at each level of higher education.
Here is a breakdown of each program:
Bachelor’s in Business Administration with Business Analytics Major
For those leaving school or with no higher education experience, a bachelor’s where you major in business analytics is the advised move. At Hult, our core program is centered around challenge learning, and you can major or minor in business analytics. It’s designed to give you the fundamentals associated with a career in business analytics.
Some key modules are:
- Collecting, Building & Sorting Data
- Machine Learning Techniques
- Data Modelling & Interpreting Data
- Relational Database Management Systems
- Visualization of Data to Influence Decisions
These modules are designed to equip you with a full range of skills in data analytics. These skills range from artificial intelligence and big data to spreadsheet modeling and data visualization. A bachelor’s with this as a major is the perfect way to launch a successful career in business analytics.
See the extent of Hult’s Bachelor of Business Administration with a major in business analytics here:
Master’s in Business Analytics
The next step up if you are looking for a more advanced course on business analytics would be a master’s program. Hult’s Master’s in Business Analytics is available for those who have already taken part in higher education and wish to enhance their knowledge. This is Hult’s only course where all core modules are geared toward the study of business analytics and is for those set on a career in the practice.
The three core modules are:
1.) Data Fundamentals—a thorough introduction to the world of data
2.) Data Mastery—the study of data through practical challenges, mastering visualization, and algorithms
3.) Data Impact—study focused on data optimization through machine learning and leadership skills
The core modules listed should delve deeply into Python and other data languages and should give you the skills and knowledge to understand and interpret data. Hult’s Master’s in Business Analytics and other specialized courses are for those seriously considering a specialized career.
Check this Business Analytics Master Class delivered by Professor Omar Hernandez:
An MBA is a specialized business degree created with the business leaders of tomorrow in mind. One of the key skills needed from a modern business professional is data analysis. Hult’s MBA programs offer electives to cover all ranges of the business spectrum, and any quality MBA, like Hult’s, would naturally offer one in business analytics.
The electives in business analytics are:
- Behavioral Economics & Decision Making
- Business Intelligence
- Data Strategy
- Data Visualization
- Introduction to Python
- Introduction to R
- Marketing Analytics
- Supply Chain Analytics
Business leaders need to be well-rounded, but this doesn’t mean you can’t be a specialist with an MBA. Picking electives solely centered around business analytics is one of the many diverse options available to you to suit your personal goals.
Dual Degree in Business Analytics
Double your chances in the global job market with a Dual Degree, which sees you earn two triple-accredited degrees in as little as 18 months.
If you choose to further your studies with a full-time Dual Degree program, your first degree will follow a standard one-year master’s program or Global One-Year MBA program, with the same home campus options and the opportunity to take any electives at any of our six campuses. You’ll then pursue your accelerated second degree, which has no elective courses, at our London, Boston, or San Francisco campus.